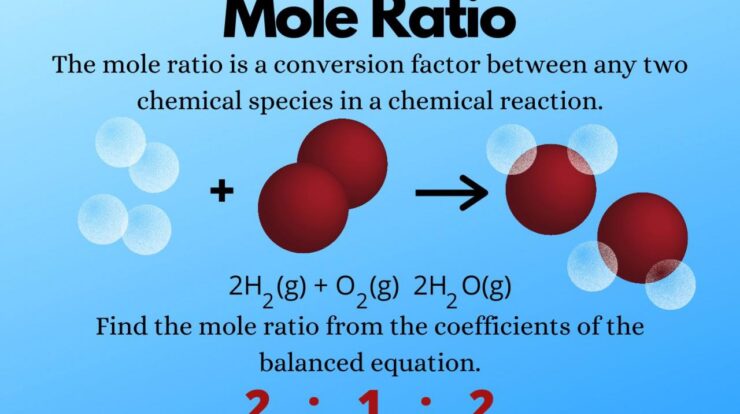
Mole measurement, the cornerstone of quantitative chemistry, unlocks a world of precise understanding and scientific discovery. This fundamental concept empowers scientists to unravel the intricate details of matter, enabling advancements in fields ranging from chemistry and biology to medicine and materials science.
Delving into the depths of mole measurement, we explore its significance, methods, applications, and advanced techniques, unraveling the mysteries of the molecular world.
Mole Measurement: A Fundamental Tool in Science
The concept of moles plays a pivotal role in chemistry and various scientific disciplines, providing a standardized unit for quantifying the amount of substance. Mole measurement enables precise determination of the number of atoms, molecules, or ions present in a given sample, facilitating accurate analysis and understanding of chemical reactions and processes.
Definition and Importance of Mole Measurement
A mole is defined as the amount of substance that contains exactly 6.02214076 × 10 23elementary entities. These entities can be atoms, molecules, ions, or electrons, depending on the context. The mole serves as a convenient and universal unit for expressing the quantity of substances involved in chemical reactions, ensuring consistency and accuracy across scientific disciplines.
Mole measurement is crucial in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and environmental science. It allows scientists to determine the molar mass of compounds, calculate concentrations of solutions, and balance chemical equations. By understanding the number of moles present in a sample, researchers can gain insights into the stoichiometry and thermodynamics of chemical reactions, facilitating the prediction and analysis of reaction outcomes.
Methods for Determining Mole Measurement
There are several methods employed to determine the number of moles in a sample. Gravimetric analysis involves measuring the mass of a substance and using its molar mass to calculate the number of moles. Volumetric analysis, on the other hand, involves measuring the volume of a solution that reacts with the substance of interest.
Titration, a specific type of volumetric analysis, is commonly used to determine the concentration of a solution by gradually adding a known volume of a reagent until the reaction is complete.
Factors Affecting Mole Measurement Accuracy
The accuracy of mole measurement can be influenced by several factors. Temperature, pressure, and purity of the sample can all impact the results. It is essential to control these variables and minimize potential sources of error to ensure precise and reliable mole measurements.
Applications of Mole Measurement
Mole measurement finds applications in a wide range of fields, including chemistry, biology, and environmental science. In chemistry, it is used in stoichiometric calculations to determine the amounts of reactants and products involved in chemical reactions. In biology, mole measurement is crucial for determining the concentration of solutions used in experiments and for understanding the molecular composition of cells and organisms.
Advanced Techniques in Mole Measurement
In addition to traditional methods, advanced analytical techniques such as spectrophotometry and chromatography have been developed for precise mole measurement. Spectrophotometry measures the absorption or emission of light by a substance, while chromatography separates and analyzes components of a mixture based on their different physical properties.
These techniques provide accurate and sensitive mole measurements, enabling detailed analysis of complex samples.
Summary
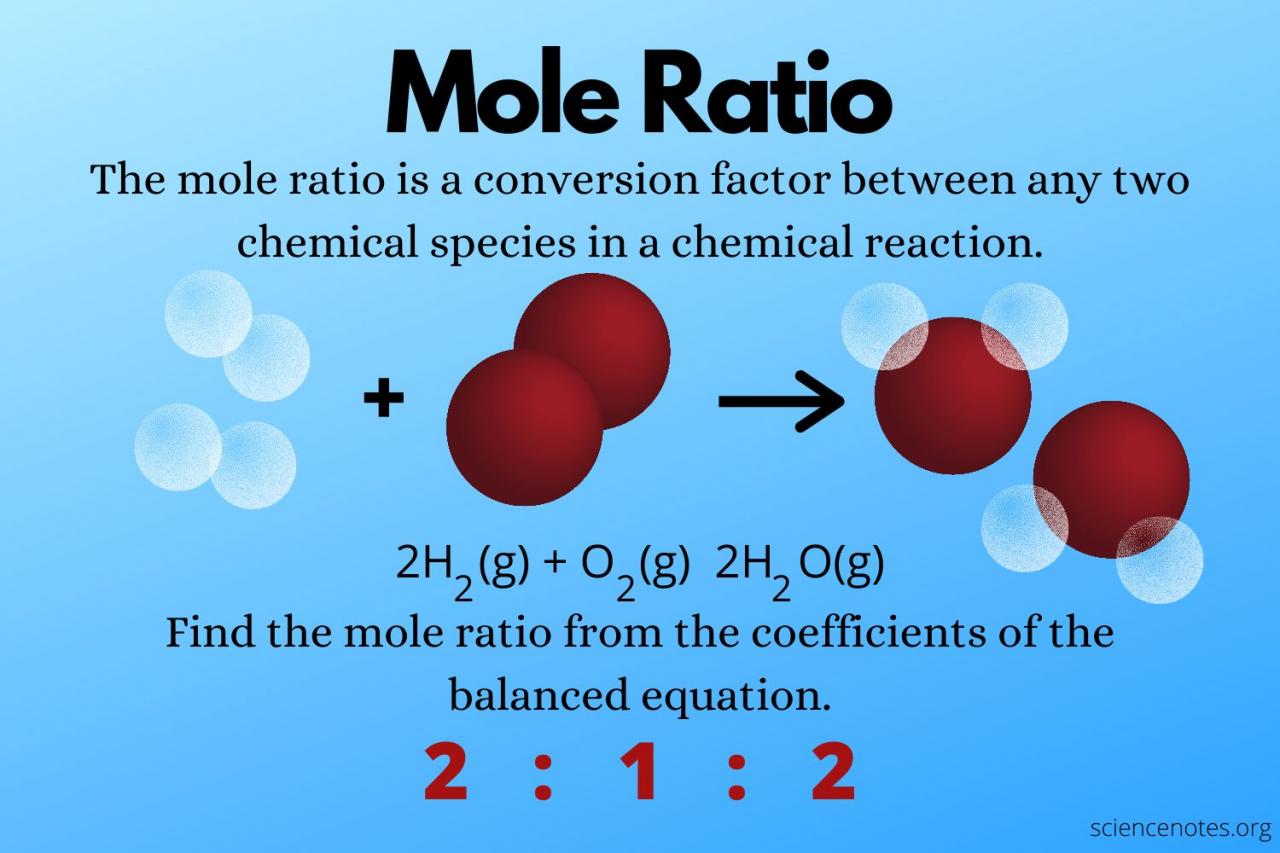
Mole measurement stands as a testament to the power of scientific inquiry, providing a precise and reliable means to quantify substances and unravel the fundamental building blocks of our universe. Its versatility and accuracy have revolutionized our understanding of matter and continue to drive scientific breakthroughs that shape our world.
Questions Often Asked: Mole Measurement
What is the significance of mole measurement?
Mole measurement provides a precise and consistent way to quantify substances, enabling accurate determination of their composition, reactivity, and other properties.
How is mole measurement determined?
Mole measurement can be determined using various methods, including gravimetric analysis, volumetric analysis, and titration, each with its own advantages and applications.
What factors can affect the accuracy of mole measurement?
Temperature, pressure, and the purity of the substance being measured can all impact the accuracy of mole measurement, highlighting the importance of careful experimental techniques.
What are some applications of mole measurement?
Mole measurement finds widespread use in chemistry, biology, and other fields, including stoichiometric calculations, determining molecular weights, and understanding chemical reactions.